
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.
In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. According to this definition, noble gas atoms are considered molecules as they are mono-atomic molecules.
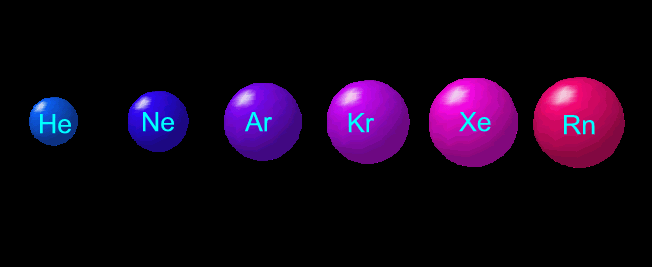
Several types of non-metal elements exist only as molecules in the environment. For example, hydrogen only exists as hydrogen molecule (H₂). A molecule may be homo-nuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, as with oxygen (O₂).
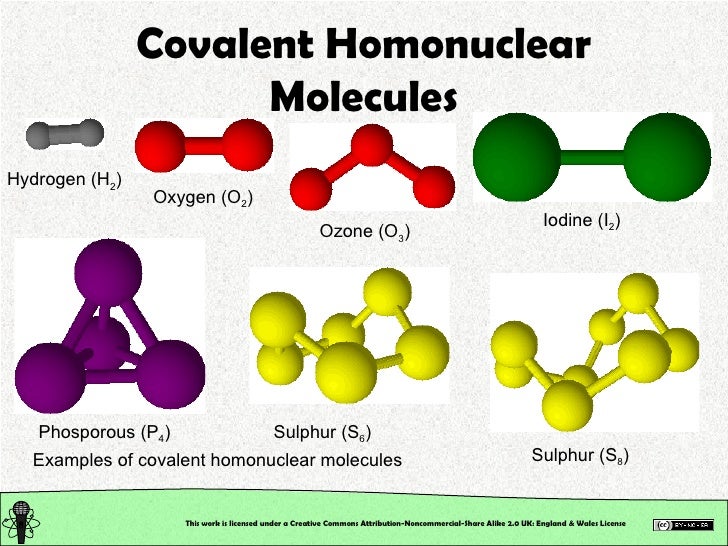
A molecule of a compound is made out of two or more elements. It may be hetero-nuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, like as water (H₂O).
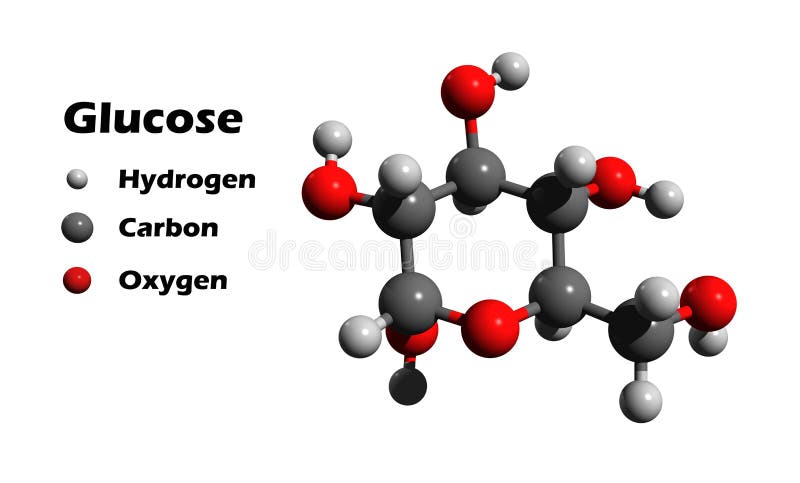
The chemical formula for a molecule uses one line of chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to one typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. With a molecular formula, you can write down the numbers of all atoms in a molecule. For example, the molecular formula of glucose is C₆H₁₂O₆. That means that one molecule of glucose is made up of six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms.
In gases like air, the molecules are just flying around. In liquids like water, the molecules are stuck together but they can still move. In solids like sugar, the molecules can only vibrate. Molecules are held together by either covalent bonding or ionic bonding.
- Covalent Bonding
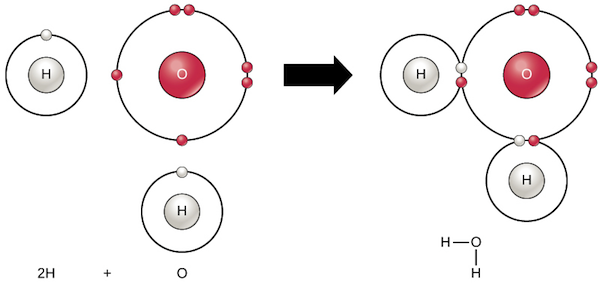
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed covalent bonding.
- Ionic Bonding
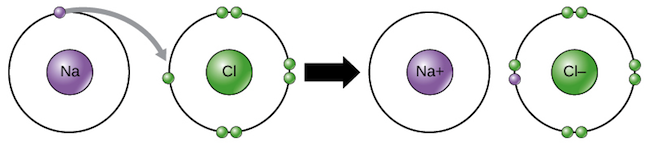
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The positive ions are the atoms that have lost one or more electrons which also termed as cations whereas the negative ions are the atoms that have gained one or more electrons which also termed as anions. This transfer of electrons is termed as electro-valence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom such as in Sodium chloride (NaCl), but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH₄⁺ or SO₄²⁻ from the molecule Ammonium sulphate [ (NH₄)₂ SO₄ ] .
Comments
Post a Comment